What Is DSN? in both military and technology contexts, clears up secondary terms like army DSN, DSN military, and open DSN, and answers all the common questions people are Googling today. And yes, we’ll even throw in real-world examples, a few pro tips, and a little humor.
What Is a DSN? Understand the Dual Definitions
There’s a reason for the confusion — DSN doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all meaning. Let’s begin by breaking down the two most widely used versions:
1. DSN in the Military: Defense Switched Network
In this context, DSN means the Defense Switched Network, which is an internal communication system used by the U.S. Department of Defense.
Think of it as the military’s global phone system — highly resilient, secure, and separate from regular commercial telephone networks.
2. DSN in Technology: Data Source Name
If you’re a web developer, database admin, or working with SQL databases, DSN refers to the Data Source Name — a set of parameters that define how to connect an application to a database through ODBC (Open Database Connectivity).
So, depending on who you ask — or where you’re working — DSN can either secure a network call or pull data from MySQL.
Pretty wild, right?
“When I started my IT career in the Air Force and someone asked about DSN access, I thought they meant database settings. They really meant making global calls!” – a sysadmin on a tech forum.
DSN Military: The Lifeline of Defense Communication
Let’s dive deeper into DSN military use.
What Is the Army DSN?
Army DSN is simply the branch-specific implementation of the larger Defense Switched Network. Every U.S. Army base — whether in Kansas or South Korea — is connected via DSN lines to ensure fast, secure, real-time communication.
Features of the Defense Switched Network:
- Secure telephony between U.S. government locations
- Up 99.99% reliability with built-in redundancies
- Voice, data, video, and messaging capabilities
- Internationally deployed with global access
Unlike commercial phone systems, DSN is an infrastructure specifically designed for mission-critical ops. Even during emergencies or cyber attacks, the network remains operational. That’s why troop communications, embassy calls, and military command centers rely on DSN every day.
Understanding DSN Dialing: How to Use It
When making calls on the DSN system, dialing works differently. A DSN number usually looks like:
textDSN: 312-567-1234
In this case:
- 312 = Area code
- 567-1234 = Local number on base
Depending on your location, you might need a routing prefix or access code to reach different installations.
There’s a whole DSN directory used across branches to track which base uses which area code. And if you’re on a military-connected VoIP or remote system in 2025? DSN routing is often automated through SIP now.
DSN in Tech: What Is a Data Source Name?
Shifting gears to our tech-focused readers — let’s answer what is a DSN in software and database terms.
TL;DR:
DSN = Data Source Name
It’s a configuration setting that tells an application how to connect to a specific database using ODBC.
Example DSN Setup:
If you’re building a PHP app, you might set:
PHP$dsn = 'mysql:host=localhost;dbname=inventory';
$user = 'admin';
$password = 'securepass';
In this case, the DSN defines the database type, server location, and name.
This is crucial for:
- Web developers (PHP, Python, Node.js)
- BI tools (Power BI, Tableau)
- Admins working with ETL processes or APIs
- Cloud-hosted applications using remote DBs
How Does DSN Compare to Direct DB Connections?
Without DSN, you’d make a manual connection every time — needing to set hostnames, ports, and credentials all over again.
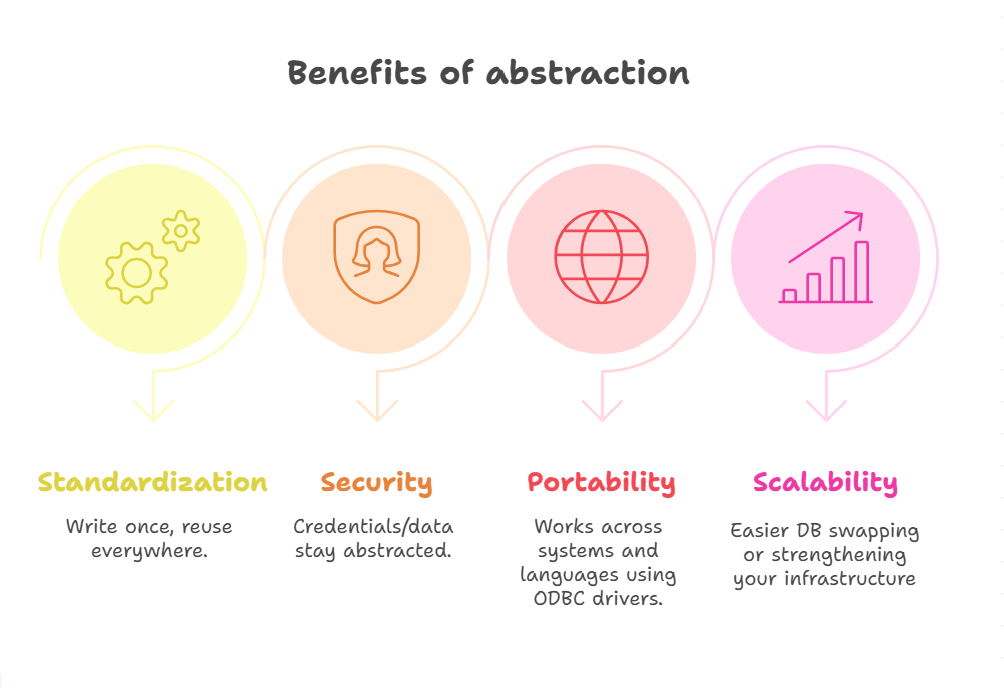
Benefits of DSN in IT:
- Standardization: Write once, reuse everywhere.
- Security: Credentials/data stay abstracted.
- Portability: Works across systems and languages using ODBC drivers.
- Scalability: Easier DB swapping or strengthening your infrastructure.
Whether you’re in a military office or a cloud container, DSN saves time, reduces errors, and tightens control.
What Is Open DSN? (And Should You Be Concerned?)
If you’ve seen the term “open DSN” floating around, it depends which world you’re in:
In Military/Comms:
Open DSN may refer to open or unrestricted use of Defense Switched Network lines between installations or units, as opposed to restricted channels or encrypted endpoints.
In Tech:
Open DSN could mean either:
- A system where Data Source Name credentials are accessible (possibly a security risk)
- A DSN string in a config file without a login requirement
Either way, best advice: You don’t want your DSNs to be “open” unless you know exactly who can access them.
Real-World Example: Dual Use of DSN in Action
Let’s paint a scenario.
Robert is an Army contractor managing a logistics platform hosted on AWS GovCloud. He needs to:
- Dial into an embassy station using a DSN voice line for a coordination call.
- Set up an ODBC DSN connection string for pulling location-based inventory from a remote Microsoft SQL Server.
Both tasks involve DSN — but in completely separate verticals.
He jokes:
“DSN helps me make the call AND pull the data I’m referencing in it. Pretty meta, right?”
Yep. That’s DSN in 2025. Misunderstand it, and you lose time. Master it? You save operations.
Pros and Cons of DSN (Military and Tech)
Benefits:
- Military DSN: High availability, mission-critical reliability, global scope
- Tech DSN: Simplifies database config, improves security, standardizes access
- Both share one key trait: structured accuracy
Drawbacks/Risks:
- Army DSN access is typically restricted; requires clearance
- Open DSN in software could expose sensitive data if misconfigured
- Troubleshooting DSN-based issues in IT environments can be tricky without proper documentation
Always label your DSNs clearly and securely.
Common Use Cases for DSN in 2025
Military/Government:
- Inter-base secure communication
- International embassy coordination
- Encrypted VoIP installations
- Worldwide command logistics
Tech/Enterprise:
- Web app database connections
- Centralized reporting via Power BI/Tableau
- Automated ETL pipelines
- Secure credential abstraction
FAQs
Q1: What is a DSN and how is it used in the Army?
A: In the Army, DSN refers to the Defense Switched Network, used for secure calls and communication between military installations. It’s separate from commercial phone systems and used globally.
Q2: What is a DSN in programming or IT?
A: In programming, DSN stands for Data Source Name. It’s a string of information required to connect an app or software system to a database using ODBC, like MySQL or SQL Server.
Q3: Is the DSN system still in use in 2025?
A: Absolutely. The Defense Switched Network is alive and well — although increasingly integrated with secure VoIP, satellite, and SIP-based technologies for faster, multi-channel operations.
Q4: What’s the difference between DSN and IP communication?
A: DSN (in military context) uses circuit-switched systems for secure voice. IP communication uses packets — more flexible but less secure inherently. DSN is still preferred in mission-critical government ops.
Final Thoughts
So, if someone asks you, “What is DSN?” — now you can confidently say:
“It depends.”
In one universe, it’s how the military talks between continents. In another, it’s how a web app securely pulls weather data from a PostgreSQL database.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
There’s a certain weight in the words John Authers writes—not just because of what he knows, but how he shares it. His voice doesn’t just echo facts; it builds meaning. In a world overwhelmed by rushed opinions and robotic summaries, John’s writing feels… different. It feels lived-in, thoughtful, and deeply human.
Readers don’t turn to John for headlines—they come for context. They come for that rare blend of clarity, insight, and emotional depth that turns financial journalism into something closer to storytelling. His reflections on markets, geopolitics, or human behavior aren’t just readable—they’re relatable.
What sets John apart isn’t just his experience (though he has plenty of it). It’s his ability to pause, reflect, and explain the why behind the what. He writes like someone who’s been in the room where it happens—but never forgets the reader who hasn’t.
In 2025, when AI churns out articles in milliseconds, John Authers still writes like a human—and that, more than anything, is what makes his work worth reading.